In computing, and specifically in the context of Microsoft Windowsoperating systems, Microsoft refers to Folder Redirection when automatically re-routing I/O to/from standard folders (directories) to use storage elsewhere on a network.[1]
It is often used in an office network environment, to ensure that users do not store data locally, when a network device is the preferred storage location. Folder Redirection allows saving data regardless of storage location and separates user data from profile data decreasing the time required to log on.
Other advantages include:[2]
When Folder Redirection is implemented (Folder Redirection Module in ProfileUnity) for Windows 10, and 'User's Files' setting is enabled on the desktop (Desktop Icon Settings). The folders inside 'User's Files' section will point to local shell folders instead of file shares on the server. Symptoms: This was tested with Version 1703 of Windows 10. Folder Redirection processing contains five steps: Determine which user folders to redirect based on changes to Group Policy settings at the time. Determine the target location specified for redirection and confirm the user has access rights. If the target folder does not exist, the folder is. Also apply redirection policy to Windows 2000, Windows 2000 server, Windows XP, and Windows Server 2003 operating systems: Disabled Policy Removal Behavior: Restore contents Documents Setting: Basic (Redirect everyone's folder to the same location) Path: domain.local Drives RedirectedFolders adam.marshall Documents. Folder redirection. Windows XP also implements a Recycle Bin for the My Documents folder. Windows Vista introduces the ability to independently redirect up to 10 user profile sub-folders to a network location. There is also a Management Console snap-in in Windows Vista to allow users to configure Folder Redirection for clients running Windows Vista. According to Folder redirection,folder redirection is often used in an office network environment, to ensure that users do not store data locally, when a network device is the preferred storage location. Folder Redirection allows saving data regardless of storage location and separates user data from profile data decreasing the time required to log on.
Jan 12, 2017 I have successfully created a folder redirection GPO for a OU and this works fine in Windows 8 clients, but it is not working in Windows 10. This seems to be a common problem and other user are experiencing. Some other possible reasons are related to WMI filtering but the I am not sure if some WMI filter are being applied. Click the Group Policies tab, click Default Domain Policy, and then click Edit. When Group Policies starts, click User Configuration, click Windows Settings, and then click Folder Redirection. Right-click Desktop Folder, and then click Properties. You can now configure the location of the Desktop folder.
- Data is stored on a server where it can be backed up
- If the same redirection is applied to multiple users, all data is stored in the one location
- Allows for sharing of data between users directly from the server rather than creating shares on individual workstations
- Allows system administrators to spend less on workstation hard drives, and more on file server hard drives
- If all user folders are redirected and caching is disabled, no files are stored on the workstations and thus data is better protected from theft
Under Microsoft Windows, the redirection is often performed by Group Policy,[3] when used in an Active Directory environment. It can also be performed by manually editing the Windows Registry, changing library locations,[4] or with tools such as Tweak UI. Disk quotas can be used to limit the amount of space taken up by users' special folders. The %username% and %userprofile%environment variables can also be used with Folder Redirection.
Up to Windows XP, the Application Data, Desktop, My Documents, My Pictures, and Start Menuspecial folders can be redirected to a file server. Windows XP also implements a Recycle Bin for the My Documents folder.
Windows Vista introduces the ability to independently redirect up to 10 user profile sub-folders to a network location.[5] There is also a Management Console snap-in in Windows Vista to allow users to configure Folder Redirection for clients running Windows Vista, Windows XP, and Windows 2000. Each redirected folder in Vista and later also has a Recycle Bin associated with it.
Under Windows 7 and later, the following user folders may be redirected: AppData/Roaming, Contacts, Desktop, Downloads, Favorites, Links, Music, Documents, Pictures, Saved Games, Searches, Start Menu, and Videos.[6]
The equivalent functionality is achieved in Unix-like systems by using mount or ln and a NFS or CIF.
See also[edit]
References[edit]
- ^Folder Redirection in Windows
- ^Folder Redirection Overview
- ^How to dynamically create security-enhanced redirected folders by using folder redirection in Windows
- ^Customize a library
- ^Managing Roaming User Data Deployment GuideArchived 2008-04-05 at the Wayback Machine
- ^Microsoft TechNet: Folder Redirection Overview
Applies to: Windows 10, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 8.1, Windows Vista, Windows Server 2019, Windows Server 2016, Windows Server 2012, Windows Server 2012 R2, Windows Server 2008 R2, Windows Server (Semi-annual Channel)
This topic describes how to use Windows Server to deploy Folder Redirection with Offline Files to Windows client computers.
For a list of recent changes to this topic, see Change history.
Important
Due to the security changes made in MS16-072, we updated Step 3: Create a GPO for Folder Redirection of this topic so that Windows can properly apply the Folder Redirection policy (and not revert redirected folders on affected PCs).
Prerequisites
Hardware requirements
Folder Redirection requires an x64-based or x86-based computer; it is not supported by Windows® RT.
Software requirements
Folder Redirection has the following software requirements:
- To administer Folder Redirection, you must be signed in as a member of the Domain Administrators security group, the Enterprise Administrators security group, or the Group Policy Creator Owners security group.
- Client computers must run Windows 10, Windows 8.1, Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Server 2019, Windows Server 2016, Windows Server (Semi-annual Channel), Windows Server 2012 R2, Windows Server 2012, Windows Server 2008 R2, or Windows Server 2008.
- Client computers must be joined to the Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) that you are managing.
- A computer must be available with Group Policy Management and Active Directory Administration Center installed.
- A file server must be available to host redirected folders.
- If the file share uses DFS Namespaces, the DFS folders (links) must have a single target to prevent users from making conflicting edits on different servers.
- If the file share uses DFS Replication to replicate the contents with another server, users must be able to access only the source server to prevent users from making conflicting edits on different servers.
- When using a clustered file share, disable continuous availability on the file share to avoid performance issues with Folder Redirection and Offline Files. Additionally, Offline Files might not transition to offline mode for 3-6 minutes after a user loses access to a continuously available file share, which could frustrate users who aren't yet using the Always Offline mode of Offline Files.
Note
Some newer features in Folder Redirection have additional client computer and Active Directory schema requirements. For more info, see Deploy primary computers, Disable Offline Files on folders, Enable Always Offline mode, and Enable optimized folder moving.
Step 1: Create a folder redirection security group
If your environment is not already set up with Folder Redirection, the first step is to create a security group that contains all users to which you want to apply Folder Redirection policy settings.
Here's how to create a security group for Folder Redirection:
- Open Server Manager on a computer with Active Directory Administration Center installed.
- On the Tools menu, select Active Directory Administration Center. Active Directory Administration Center appears.
- Right-click the appropriate domain or OU, select New, and then select Group.
- In the Create Group window, in the Group section, specify the following settings:
- In Group name, type the name of the security group, for example: Folder Redirection Users.
- In Group scope, select Security, and then select Global.
- In the Members section, select Add. The Select Users, Contacts, Computers, Service Accounts or Groups dialog box appears.
- Type the names of the users or groups to which you want to deploy Folder Redirection, select OK, and then select OK again.
Step 2: Create a file share for redirected folders
If you do not already have a file share for redirected folders, use the following procedure to create a file share on a server running Windows Server 2012.

Note
Some functionality might differ or be unavailable if you create the file share on a server running another version of Windows Server.
Here's how to create a file share on Windows Server 2019, Windows Server 2016, and Windows Server 2012:
Redirect Documents Folder Windows 10
In the Server Manager navigation pane, select File and Storage Services, and then select Shares to display the Shares page.
In the Shares tile, select Tasks, and then select New Share. The New Share Wizard appears.
On the Select Profile page, select SMB Share – Quick. If you have File Server Resource Manager installed and are using folder management properties, instead select SMB Share - Advanced.
On the Share Location page, select the server and volume on which you want to create the share.
On the Share Name page, type a name for the share (for example, Users$) in the Share name box.
Tip
When creating the share, hide the share by putting a
$after the share name. This will hide the share from casual browsers.On the Other Settings page, clear the Enable continuous availability checkbox, if present, and optionally select the Enable access-based enumeration and Encrypt data access checkboxes.
On the Permissions page, select Customize permissions…. The Advanced Security Settings dialog box appears.
Select Disable inheritance, and then select Convert inherited permissions into explicit permission on this object.
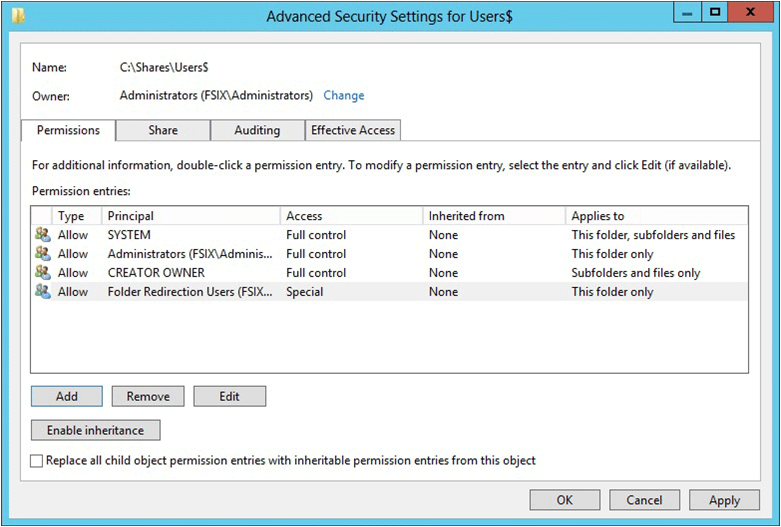
Set the permissions as described Table 1 and shown in Figure 1, removing permissions for unlisted groups and accounts, and adding special permissions to the Folder Redirection Users group that you created in Step 1.
Figure 1 Setting the permissions for the redirected folders share
If you chose the SMB Share - Advanced profile, on the Management Properties page, select the User Files Folder Usage value.
If you chose the SMB Share - Advanced profile, on the Quota page, optionally select a quota to apply to users of the share.
On the Confirmation page, select Create.
Required permissions for the file share hosting redirected folders
| User Account | Access | Applies to |
|---|---|---|
| User Account | Access | Applies to |
| System | Full control | This folder, subfolders and files |
| Administrators | Full Control | This folder only |
| Creator/Owner | Full Control | Subfolders and files only |
| Security group of users needing to put data on share (Folder Redirection Users) | List folder / read data (Advanced permissions) Create folders / append data (Advanced permissions) Read attributes (Advanced permissions) Read extended attributes (Advanced permissions) Read permissions (Advanced permissions) | This folder only |
| Other groups and accounts | None (remove) |
Step 3: Create a GPO for Folder Redirection
If you do not already have a GPO created for Folder Redirection settings, use the following procedure to create one.
Here's how to create a GPO for Folder Redirection:
Open Server Manager on a computer with Group Policy Management installed.
From the Tools menu, select Group Policy Management.
Right-click the domain or OU in which you want to setup Folder Redirection, then select Create a GPO in this domain, and Link it here.
In the New GPO dialog box, type a name for the GPO (for example, Folder Redirection Settings), and then select OK.
Right-click the newly created GPO and then clear the Link Enabled checkbox. This prevents the GPO from being applied until you finish configuring it.
Select the GPO. In the Security Filtering section of the Scope tab, select Authenticated Users, and then select Remove to prevent the GPO from being applied to everyone.
In the Security Filtering section, select Add.
In the Select User, Computer, or Group dialog box, type the name of the security group you created in Step 1 (for example, Folder Redirection Users), and then select OK.
Select the Delegation tab, select Add, type Authenticated Users, select OK, and then select OK again to accept the default Read permissions.
This step is necessary due to security changes made in MS16-072.
Important
Due to the security changes made in MS16-072, you now must give the Authenticated Users group delegated Read permissions to the Folder Redirection GPO - otherwise the GPO won't get applied to users, or if it's already applied, the GPO is removed, redirecting folders back to the local PC. For more info, see Deploying Group Policy Security Update MS16-072.
Step 4: Configure folder redirection with Offline Files
After creating a GPO for Folder Redirection settings, edit the Group Policy settings to enable and configure Folder Redirection, as discussed in the following procedure.
Note
Offline Files is enabled by default for redirected folders on Windows client computers, and disabled on computers running Windows Server, unless changed by the user. To use Group Policy to control whether Offline Files is enabled, use the Allow or disallow use of the Offline Files feature policy setting.For information about some of the other Offline Files Group Policy settings, see Enable Advanced Offline Files Functionality, and Configuring Group Policy for Offline Files.
Here's how to configure Folder Redirection in Group Policy:
In Group Policy Management, right-click the GPO you created (for example, Folder Redirection Settings), and then select Edit.
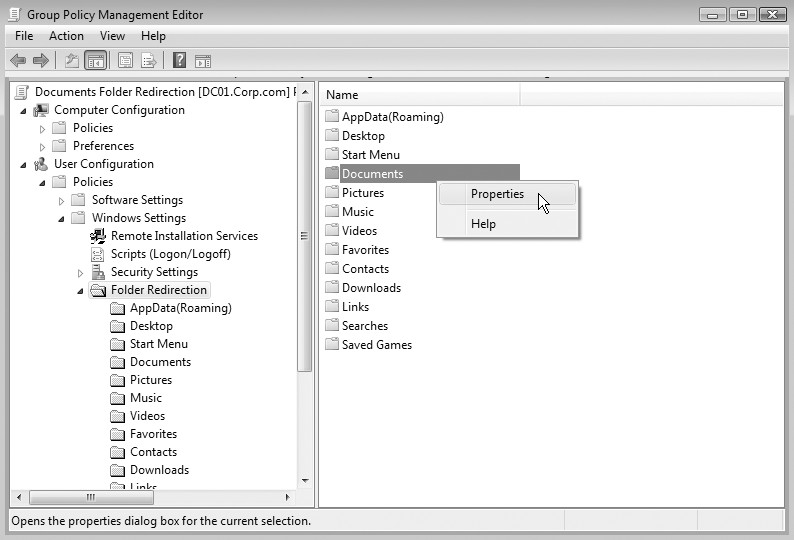
In the Group Policy Management Editor window, navigate to User Configuration, then Policies, then Windows Settings, and then Folder Redirection.
Right-click a folder that you want to redirect (for example, Documents), and then select Properties.
In the Properties dialog box, from the Setting box, select Basic - Redirect everyone's folder to the same location.
Note
To apply Folder Redirection to client computers running Windows XP or Windows Server 2003, select the Settings tab and select the Also apply redirection policy to Windows 2000, Windows 2000 Server, Windows XP, and Windows Server 2003 operating systems checkbox.
In the Target folder location section, select Create a folder for each user under the root path and then in the Root Path box, type the path to the file share storing redirected folders, for example: fs1.corp.contoso.comusers$
Select the Settings tab, and in the Policy Removal section, optionally select Redirect the folder back to the local userprofile location when the policy is removed (this setting can help make Folder Redirection behave more predictably for adminisitrators and users).
Select OK, and then select Yes in the Warning dialog box.
Step 5: Enable the Folder Redirection GPO
Once you have completed configuring the Folder Redirection Group Policy settings, the next step is to enable the GPO, permitting it to be applied to affected users.
Tip
If you plan to implement primary computer support or other policy settings, do so now, before you enable the GPO. This prevents user data from being copied to non-primary computers before primary computer support is enabled.
Here's how to enable the Folder Redirection GPO:
- Open Group Policy Management.
- Right-click the GPO that you created, and then select Link Enabled. A checkbox will appear next to the menu item.
Step 6: Test Folder Redirection
To test Folder Redirection, sign in to a computer with a user account configured for Folder Redirection. Then confirm that the folders and profiles are redirected.
Here's how to test Folder Redirection:
Sign in to a primary computer (if you enabled primary computer support) with a user account for which you have enabled Folder Redirection.
If the user has previously signed in to the computer, open an elevated command prompt, and then type the following command to ensure that the latest Group Policy settings are applied to the client computer:
Open File Explorer.
Right-click a redirected folder (for example, the My Documents folder in the Documents library), and then select Properties.
Select the Location tab, and confirm that the path displays the file share you specified instead of a local path.
Appendix A: Checklist for deploying Folder Redirection
| Status | Action |
|---|---|
| ☐ ☐ ☐ | 1. Prepare domain - Join computers to domain - Create user accounts |
| ☐ | 2. Create security group for Folder Redirection - Group name: - Members: |
| ☐ | 3. Create a file share for redirected folders - File share name: |
| ☐ | 4. Create a GPO for Folder Redirection - GPO name: |
| ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ | 5. Configure Folder Redirection and Offline Files policy settings - Redirected folders: - Windows 2000, Windows XP, and Windows Server 2003 support enabled? - Offline Files enabled? (enabled by default on Windows client computers) - Always Offline Mode enabled? - Background file synchronization enabled? - Optimized Move of redirected folders enabled? |
| ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ | 6. (Optional) Enable primary computer support - Computer-based or User-based? - Designate primary computers for users - Location of user and primary computer mappings: - (Optional) Enable primary computer support for Folder Redirection - (Optional) Enable primary computer support for Roaming User Profiles |
| ☐ | 7. Enable the Folder Redirection GPO |
| ☐ | 8. Test Folder Redirection |
Change history
The following table summarizes some of the most important changes to this topic.
Windows Folder Redirection Registry
| Date | Description | Reason |
|---|---|---|
| January 18, 2017 | Added a step to Step 3: Create a GPO for Folder Redirection to delegate Read permissions to Authenticated Users, which is now required because of a Group Policy security update. | Customer feedback |